In Vitro Fertilization: Do You Know What It Is?
In vitro fertilization enables the birth of one million children each year. But do you know how to perform them and what risks may be associated with it?
In vitro fertilization is the fertilization of an egg with sperm outside the mother’s uterus. This laboratory process helps couples with fertility problems to get pregnant.
Louise Brown, the daughter of Leslie and John Brown, is the first person to be born through in vitro fertilization (IVF). This happened on July 25, 1978 at Oldham General Hospital in Manchester, England.
Since then, according to data presented by the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE) in 2018, more than 8 million babies have been born worldwide thanks to this technique.
When is IVF used?
IVF is usually used when other, less invasive methods of fertilization, such as hormone therapy or intrauterine artificial insemination, are not working. It can be performed using the ova and sperm of a donor or couple, if either of the partners has fertility problems.
The most common causes of infertility that can be overcome with IVF are as follows:

- Destruction of the fallopian tubes: This makes it very difficult for an egg to fertilize. If an embolus occurs, it prevents the embryo from going into the uterus, preventing pregnancy.
- Ovulation problems: The body does not make enough eggs.
- Fibromas: These are benign tumors on the walls of the uterus that make it difficult for the egg to implant.
- Endometriosis: Uterine tissue grows outside of the ovaries.
- Ovarian failure: It happens when the ovaries do not produce enough eggs.
- Genetic Problems: When a man or woman has congenital diseases that they can pass on to children.
- Semen problems: The sperm count is too low or not very mobile.
- Connected fallopian tubes (associated fallopian tubes): When a woman has attached fallopian tubes, IVF may enable her to become pregnant.
- Egg preservation: If a woman is about to undergo fertility treatments for cancer, she can preserve the frozen eggs for use later for IVF.
How is IVF performed?
1. Preparation
Before embarking on the IVF process, doctors need to carry out various analyzes to make sure that both a woman and a man can fertilize during the process.
Such analyzes include detecting diseases, checking the quality of sperm, woman’s egg reserves, and examining the movement of fetuses and the condition of the uterus.
After receiving permission, the woman begins taking medications that stimulate the production of eggs and, later, the maturation of oocytes.
After preparations that take two weeks to a month, doctors will perform a transvaginal ultrasound and blood tests to prove that her body and eggs are ready for fertilization. During this time, they give her an injection of the hormone hCG, which makes the eggs mature. Then, after 36 hours, they can start the whole process.
2. Obtaining eggs
For this purpose, fertilization specialists collect the ova with a needle by insertion in the operating room under anesthesia. The whole process takes about 15 minutes.
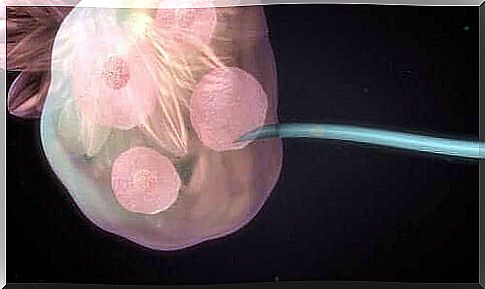
An ultrasound probe is inserted into the vagina to perform a collection. Then, with the help of an ultrasound, the doctor inserts a thin needle to reach the follicles and collect the eggs through it.
In some cases, when transvaginal ultrasound cannot be performed, doctors perform laparoscopy. It consists in making a small incision in the area of the navel. Then a fiber optic camera with a needle is inserted through it, through which the ova are collected.
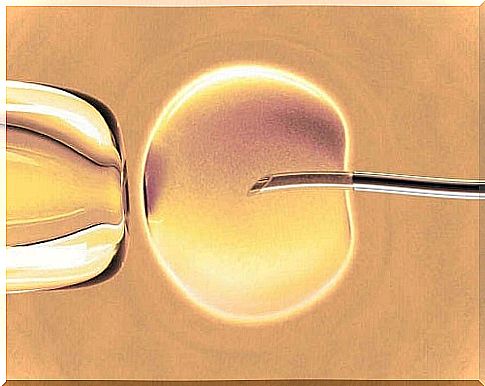
3. Fertilization
After obtaining the ova and sperm from the male, the in vitro fertilization process can begin. Semen is obtained by masturbation or, in complicated cases, by suction from the testicles. This means that the sperm is drawn directly from the testicles with a needle.
During IVF, a qualified specialist connects the mature eggs with the man’s sperm during platelet culture . It does this by using maternal serum, similar to the material found in the fallopian tubes.
The next process is the intracytoplasmic sperm administration. It involves injecting sperm directly into each egg.
Later, the embryos created as a result of the fertilization process are examined daily and selected ones are transferred to the uterus.
4. Transfer of the embryo to the uterus
Two to six days after conception, a specialist places the embryo in the woman’s uterus to begin pregnancy. They perform this procedure by inserting a catheter through the vagina into the uterus. This allows them to inject one or more embryos. The entire process is monitored under ultrasound.
If fertilization is successful, the embryo will stick to the uterine wall. Successful fertilization can be confirmed after 11 days. After this point, a normal pregnancy begins with regular follow-up visits.
Good quality embryos that have not been used are frozen. Thanks to this, they can be used later, if the couple wants to have another child, without having to repeat the entire process of ovarian stimulation. The protocols for their storage vary depending on the laws in force in a given country.
Possible complications and risks of in vitro fertilization
The likelihood of successful IVF depends on many factors. However, it is estimated that in developed countries, the average birth rate for any IVF process ranges from 41% to 43% for women under 40 years of age. For women over 40, the rate drops to 18%.
Overall, the American Pregnancy Association warns of the following risks:
- The likelihood of multiple pregnancies caused by stimulation of fertility and implantation of various embryos. This increases the risk of premature delivery and the low birth weight of the baby.
- A slightly higher rate of miscarriage than in a normal pregnancy, especially in women over the age of 40.
- Inflammation of the vagina, kidneys or urinary system caused by errors in using a needle. They don’t occur often, but they can happen.
- Ectopic pregnancy, i.e. implantation of the embryo outside the uterus.
In addition, there are some side effects such as slight bleeding in the first days of pregnancy, dizziness, nausea, diarrhea or constipation. If you experience such problems, you should contact your gynecologist. However, they are usually not serious.