Choroiditis – Diagnosis And Treatment
Uveitis affects the eyeball that is situated between the retina and the white of the eye. According to data provided on medical portals, the disease manifests itself in redness of the eye, blurred vision and pain. In addition, it deteriorates quickly.
Studies have shown that the chronic form of this disease leads to complications such as cataracts and detachment of the retina. That is why it is worth knowing its symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods. Find out more!
How is uveitis done?
Uveitis is a type of inflammation of the eye. The choroid is the membrane that builds up the eyeball. It is highly vascular. Immune cells can pass through the blood vessels, causing an unwanted inflammatory reaction.
The website Clínic Barcelona provides interesting data on the prevalence of this disease. Some of them are:
- This eye disease is considered to be a rare disease by the World Health Organization (WHO).
- Together with diabetes, uveitis is the most common cause of blindness in working-age people, with a large socioeconomic impact.
- In the US, 10% of blindness is caused by uveitis.
These numbers indicate that this disease is more common than it seems. The website mentioned that there are different types of choroiditis depending on the affected area. Here they are:
- Anterior uveitis: Affects the front of the eye. It manifests itself with redness, pain and photophobia.
- Inflammation of the central part of the uveal tract: inflammation includes gelatinous candidate eye color and the vitreous humor fills. Deposits of cells causing inflammation can build up.
- Inflammation of the posterior segment of uveitis: retinitis.
- Inflammation of all uveal structures : the disease affects the front and back layers of the eye.
It’s time to look at the methods of diagnosis and treatment of this disease.
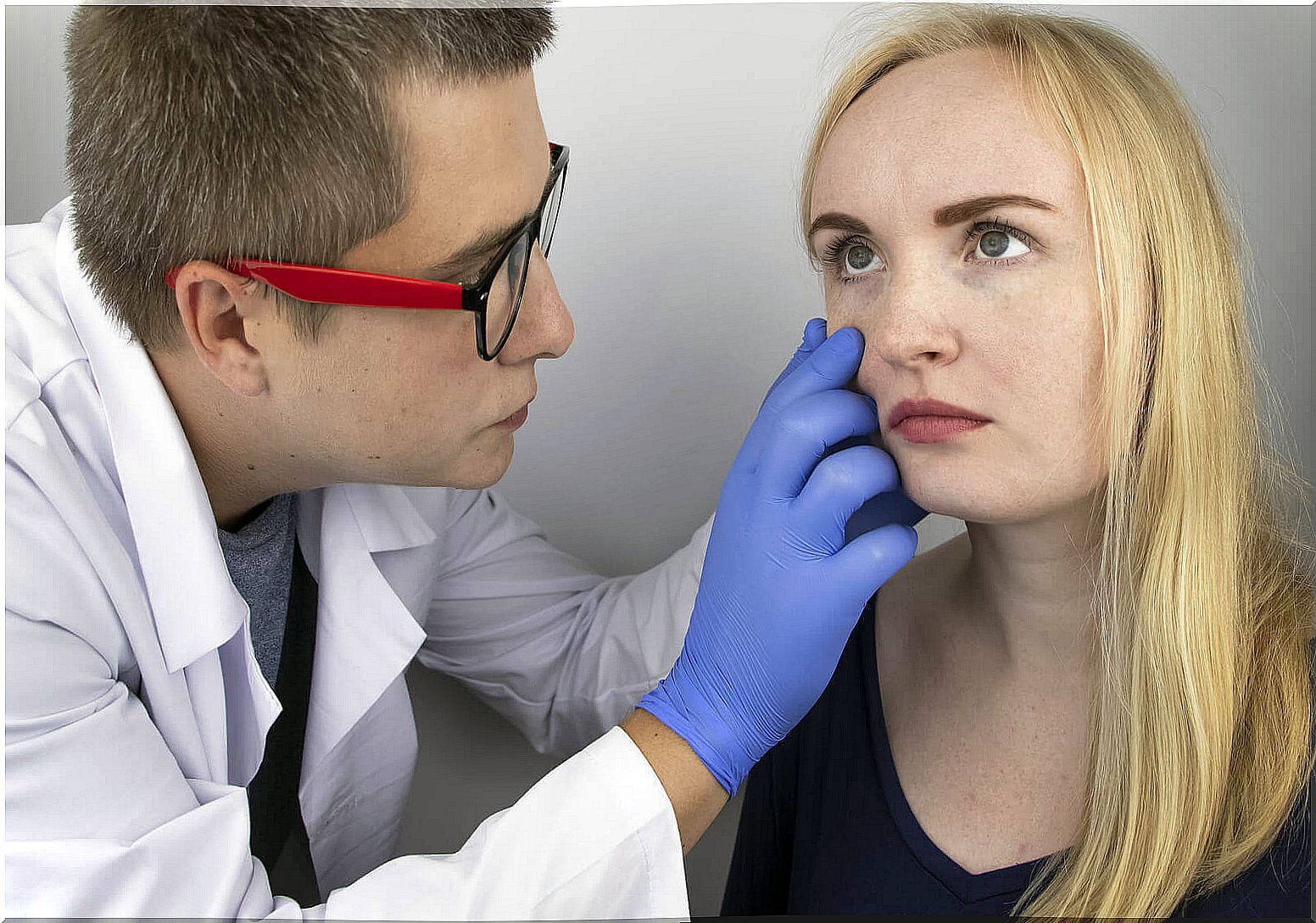
Diagnostics and treatment
The main thing is to understand the causes of this disease. The National Eye Institute (NIH) lists factors that are likely to trigger uveitis. Some of them are:
- Erroneous autoimmune reaction.
- Eye infections.
- Tumors within the eye.
- Eyeball damage.
- Contact with toxins.
- Certain diseases such as HIV, toxoplasmosis, tuberculosis and many others.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of choroiditis requires the determination of the patient’s medical history, as the causes vary and can combine. First, the eye should be examined as this disease leads to blindness.
The ophthalmologist may recommend various tests. For example:
- Visual acuity test .
- Fundus examination.
- Measurement of intraocular pressure.
- Eye examination with a slit lamp.
Unfortunately, neurological examinations may be necessary in people with mid-uveitis. Why? Research has shown it to be one of the early symptoms of MS.
Other sources say that a blood test can help diagnose the disease. This disorder can lead to various complications. The main thing is to determine if the cause is an infection or not.
Treatment
Treatment for uveitis is about fighting inflammation, relieving pain, and preventing further damage. The drug to be used depends on the cause of the disease. Bacterial infection is different from disease because of an autoimmune reaction. Therefore, drugs used in this type of ailments can be divided into three groups:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: steroids in the form of eye drops.
- Antibiotics and antivirals: aimed at eliminating viruses and bacteria.
- Drugs that regulate the immune system: Immunosuppressants that affect the patient’s immune responses.
Choroiditis – summary
As you can see, uveitis is an eye disease that has many causes. This ailment is sometimes caused, among others, by bacterial infections or neurodegenerative diseases such as multiple sclerosis.
Therefore, the diagnosis and treatment of this disease is complicated. Be sure to see a doctor if you develop persistent eye pain.